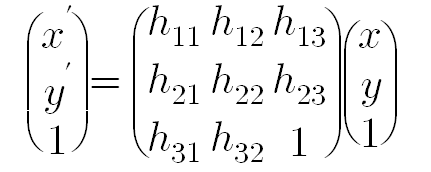OpenCV-11 Homography
by
본 포스팅은 여기, 여기 여기 를 참고하여 만들었습니다.
feature matching
keypoint는 feature에 해당하는 좌표(+그 해당 좌표에서의 정보들)을 의미하고 descriptor는 그 좌표가 지니는 정보(gradient 등) 을 나타낸다.
feature detection and feature extraction
feature detection은 이미지의 매 픽셀마다 feature가 있는지 없는지를 찾는 것 이다.
feature extraction은 차원 감소의 특별한 형태이다. 입력 데이터가 너무 큰 경우 입력 데이터를 특징 벡터, 특징 세트로 변환 하는 것을 feature extraction이라 한다. 즉 입력 데이터를 feature set으로 변환 하는 것을 feature extraction이라 한다.
즉 corner라는 feature를 찾아, 히스토그램으로 나타내는 것을 feature extraction이라 한다.
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/6832933/what-is-the-difference-between-feature-detection-and-descriptor-extraction
what is feature detector, descriptor, descriptor extractor and matcher?
feature detector : 모든 픽셀에 대해 해당 feature가 존재하는지 판단, 반복
descriptor : feature에 해당하는 픽셀을 둘러싼 주변을 설명하는 고정된 차원의 실수값 벡터
descriptor extrator : SURF, SIFT등 descriptor를 추출하는데 사용되는 각각의 알고리즘
matcher : 각 이미지에 대한 Descriptor를 매칭하는데 사용됨
flow
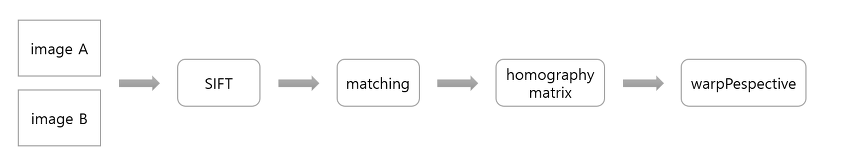
전체적인 flow는 다음과 같다.
-
Discrptor extractor인 ORB를 통해 keypoint와 descriptor를 추출한다.
-
matcher(matchGMS, BFmatcher 등)를 통해 키포인트들을 매칭한다.
-
homography matrix와, H를 추출한다.
-
H를 이미지로 변환하고 reference frame과 합친다
homography
동일한 물체에 대해서 다른 위치에서의 찍힌 두 이미지 사이의 관계는 구하는데 사용되는 알고리즘이다.
즉 2D상 임의의 사각형을 다른 임의의 사각형에 매핑 시키는 변환을 homography라 한다.
Homography를 결정하기 위해서는 최소 4개의 매칭 쌍이 필요하다.
findhomography() 함수의 경우 다수의 매칭 쌍으로부터 homography 행렬을 계산해 준다. 사용시 근사법으로는 RANSAC을 사용하였다.
https://wewinserv.tistory.com/89
나중에 공부하기
CODE
#include <librealsense2/rs.hpp>
#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <opencv2/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/videoio.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc.hpp>
#include <opencv2/features2d.hpp>
#include <opencv2/flann.hpp>
#include <opencv2/xfeatures2d.hpp>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
int main()
{
const int width = 848;
const int height = 480;
const int fps = 30;
const float depth_scale = 0.001f;
rs2::pipeline p; //비전 처리 모듈과 사용자 interaction 효과적으로 해주기 위한 pipeline 선언
rs2::config c; //config를 통해 파이프라인 스트림, 장치 선택, 필터 요청, 기기의 파이프 라인 요구 사항과 충돌이 없는지 테스트 가능
c.enable_stream(RS2_STREAM_COLOR, width, height, RS2_FORMAT_BGR8, fps); //컬러 스트림 활성화,
//RS2_FORMAT_BGR8 : 8-bit , 3channel per-pixel , 마지막 30 : 초당 가져오는 스트림 프레임
rs2::pipeline_profile profile = p.start(c); //파이프라인과 스트리밍 시작
cv::Mat frame_Ref; //레퍼런스 프레임 선언
bool is_applied = false; //is_applied가 1이 되면 current frame을 복사야여 freme_Ref에 담고 if (!frame_Ref.empty()) 문 동작
while (1)
{
rs2::frameset frameset = p.wait_for_frames(); //frameset 객체 선언, 새 프레임세트를 사용할 수 있을 떄 까지 기다리기
if (frameset)
{
auto color_frame = frameset.get_color_frame(); //video_frame으로 color_frame이란 객체 선언하여 컬러로 받음
cv::Mat frame_Cur = cv::Mat(cv::Size(width, height), CV_8UC3, (void*)color_frame.get_data()); //color_frame을 M<at에 복사하여 가져옴
if (!frame_Ref.empty()) //frame_Ref가 비었으면 1..... 안비었으면 이 문 들어옴
{
//cv::Ptr<cv::Feature2D> feature;
//cv::Ptr<cv::DescriptorMatcher> matcher;
std::vector<cv::KeyPoint> kpRef, kpCur; //done
cv::Mat descRef, descCur; //done
std::vector<cv::DMatch> matches, matchesGMS; //done
// for visualization
cv::Mat frameMatches;
//FEATURE MATCHING.
Ptr<ORB> orbs = ORB::create(100000);
orbs->detectAndCompute(frame_Ref, noArray(), kpRef, descRef); //keypoint1, descriptor에 값 적재
orbs->detectAndCompute(frame_Cur, noArray(), kpCur, descCur);
//for BFmatcher
//BFMatcher matcher(NORM_HAMMING, 1);
//matcher.match(descRef, descCur, matches); //두 이미지에서 최상의 일치를 얻음 (가장 일치하는것을 반환함), crossCheck
//cv::drawMatches(frame_Ref, kpRef, frame_Cur, kpCur, matches, frameMatches);
//for matchGMS
cv::Ptr<cv::DescriptorMatcher> matcher = DescriptorMatcher::create("BruteForce-Hamming"); //done
matcher->match(descRef, descCur, matches);
cv::xfeatures2d::matchGMS(frame_Ref.size(), frame_Cur.size(), kpRef, kpCur, matches, matchesGMS, 0, 0, 6.0);
cv::drawMatches(frame_Ref, kpRef, frame_Cur, kpCur,matchesGMS, frameMatches);
//homography
std::vector<cv::Point2f> Ref_pts, Cur_pts;
const int match_size = matchesGMS.size();
if (match_size < 4) //매칭된 점이 4 이하면 다시 while문 처음으로 들어감
continue;
Ref_pts.resize(match_size);
Cur_pts.resize(match_size);
//cout << matches.size() << "=========================" << kpRef.size() << "=========================" << kpCur.size() << "=========================" << matchesGMS.size() << endl;
for (int idx = 0; idx < match_size; ++idx)
{
const cv::Point2f Ref_pt = kpRef[matchesGMS[idx].queryIdx].pt; //그 idx에 해당하는 kpRef의 값 가져와서 ( , ) 에 담음
const cv::Point2f Cur_pt = kpCur[matchesGMS[idx].trainIdx].pt;
Ref_pts[idx] = Ref_pt; //이 ( , ) 값을 Ref_pts[idx]에 차곡차곡 저장
Cur_pts[idx] = Cur_pt;
}
//// FIND HOMOGRAPHY AND WARPING WITH TWO IMAGES.
cv::Mat warping_img;
Mat H = findHomography(Cur_pts, Ref_pts, RANSAC); //H에 각 인자들을 통해 구한 element를 갖는 행렬을 담는다
warpPerspective(frame_Cur, warping_img, H, frame_Ref.size()); //warping_img에 H에 의해 변환된 frame_Cur 를 담는다. output은 frame_Ref.size())의 dsize을 갖는다.
Mat result;
addWeighted(frame_Ref, 0.7, warping_img, 0.9, 0.0, result); //scale 하여 더한 후 result에 담음
cv::imshow("frameMatches", frameMatches);
cv::imshow("warping_img", result);
}
cv::imshow("frame_Cur", frame_Cur);
if (is_applied)
{
frame_Ref = frame_Cur.clone();
is_applied = false;
}
}
int key = cv::waitKey(5);
if (key == 'c')
{
is_applied = true;
}
if (key == 'd')
{
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
Subscribe via RSS